Combating Antibiotic Resistance: Strategies and Solutions
🔬 Introduction
Antibiotics have been one of the greatest medical discoveries of the 20th century. However, their overuse and misuse have led to a public health crisis: antibiotic resistance. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), more than 2.8 million antibiotic-resistant infections occur each year in the U.S., causing over 35,000 deaths.
This blog explores why antibiotic resistance is rising, its global impact, and the evidence-based strategies that the U.S. and international health communities are deploying to combat it.
🧬 What Is Antibiotic Resistance?
Antibiotic resistance occurs when bacteria evolve mechanisms to survive exposure to antibiotics designed to kill them. Over time, resistant strains like MRSA, CRE, and VRE can cause untreatable infections.
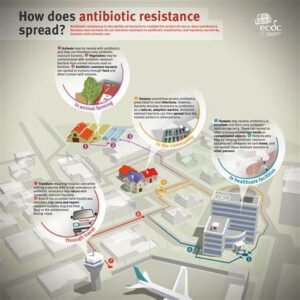
🚨 Why Is It a Global Crisis?
-
Antibiotics are losing efficacy
-
New drug development is slow
-
Routine surgeries are at higher risk
-
Cost of care rises significantly
-
Agricultural overuse adds to the problem
🔍 Causes of Antibiotic Resistance
- Overprescription in human medicine
- Patients not completing full courses
- Overuse in livestock and agriculture
- Poor infection control in hospitals
- Lack of rapid diagnostic tools
💡 Strategies to Combat Antibiotic Resistance
1. ✅ Antibiotic Stewardship Programs
Implemented in U.S. hospitals, these programs ensure responsible prescription practices.
2. 🧪 Investment in New Antibiotics
Pharmaceutical firms, supported by federal programs, are exploring new classes of antibiotics, antimicrobial peptides, and phage therapies.
3. 🐄 Regulating Antibiotic Use in Agriculture
The FDA and USDA regulate the use of antimicrobials in animal farming to prevent resistance transmission from farm to human.
4. 🦠 Surveillance and Rapid Diagnostics
Real-time global tracking of resistance patterns and faster diagnostics help prevent unnecessary prescriptions.
🔗 Global Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance System (GLASS)
5. 🌍 Public Awareness Campaigns
Education through campaigns like U.S. Antibiotic Awareness Week helps reduce self-medication and demands for unnecessary antibiotics.
🧑⚕️ Role of Healthcare Providers
Doctors and pharmacists play a pivotal role by:
-
Using narrow-spectrum antibiotics when possible
-
Avoiding antibiotics for viral infections like the common cold
-
Educating patients about proper use
🧼 Importance of Infection Prevention
Preventing infections reduces the need for antibiotics:
-
Hand hygiene
-
Sanitation
-
Safe food handling
-
Proper vaccination
💊 What Can Patients Do?
-
Never demand antibiotics for viral infections
-
Finish your entire antibiotic course
-
Never share or use leftover antibiotics
-
Avoid self-medication
📊 Resistance in Numbers
-
1 in 3 antibiotic prescriptions in the U.S. is unnecessary
-
By 2050, antimicrobial resistance could cause 10 million deaths globally
-
U.S. hospitals save millions in healthcare costs through stewardship programs